 Read more
Read more
Kinetics of Hydrogen Absorption in Individual α-Phase Palladium Nanoparticles
K. Olson*, A. Viola, E. Bellec, C. Atlan, C. Chatelier, M. Grimes, B. Gilles, T. Schülli, S. Leake, M. Vandichel, F. Maillard and M.-I. Richard*
ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2025, XXXX, XXX, XXX-XXX
Citations : 0
Kinetics of Hydrogen Absorption in Individual α-Phase Palladium Nanoparticles
Kyle J. Olson*, Arnaud Viola, Ewen Bellec, Clément Atlan, Corentin Chatelier, Michael Grimes, Bruno Gilles, Tobias U. Schülli, Steven J. Leake, Matthias Vandichel, Frédéric Maillard and Marie-Ingrid Richard*
ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2025, XXXX, XXX, XXX-XXX
-
Abstract
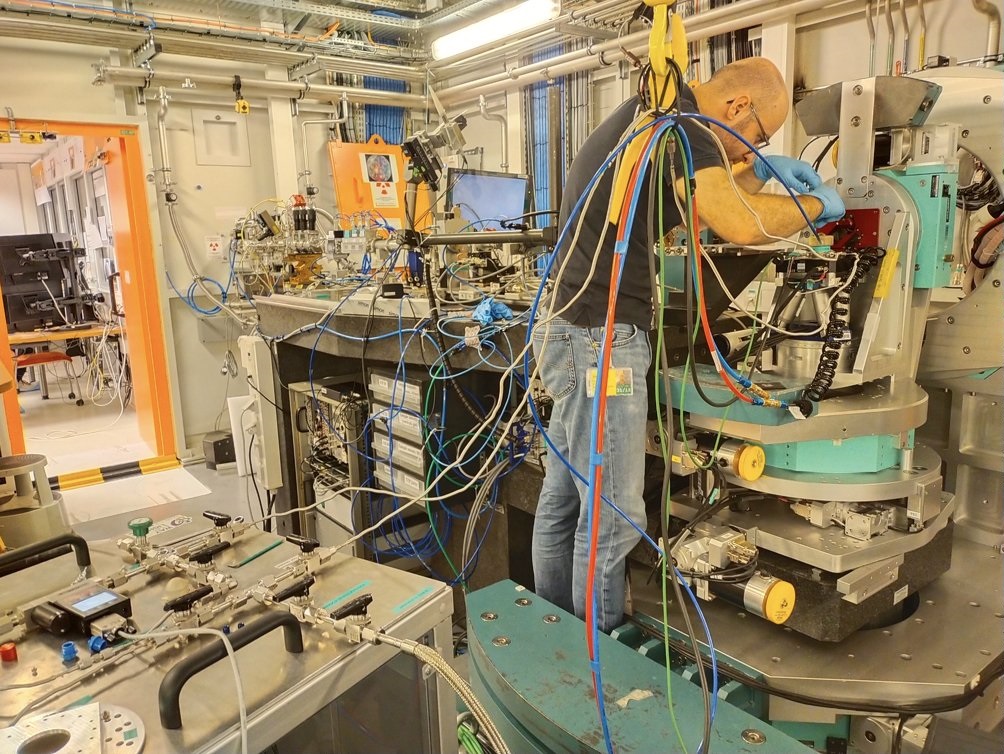
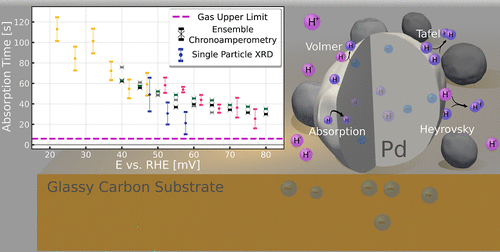
Palladium hydrogen is a useful model in the study of both hydrogen absorption for energy storage, and lattice gas systems for fundamental thermodynamic models. Using in situ time-resolved X-ray nanodiffraction at the fourth generation Extremely Brilliant Source of the European Synchrotron (ESRF-EBS), the kinetics of hydrogen absorption in individual α phase Pd nanoparticles is examined. Hydrogen absorption kinetics in a gas reactor and an electrochemical cell are compared. Combining the individual nanoparticle X-ray measurements with chronoamperometry measurements, the kinetics of the ensemble of Pd nanoparticles on the glassy carbon substrate is compared with kinetics at the single nanoparticle level. Hydrogen absorption in α phase Pd in the electrochemical system is found to be slower than that of the gas system. Furthermore, the absorption in the electrochemical system slows down as the electrochemical potential is lowered. This slow down is found to be directly related to the increasing hydrogen absorption per step in electrode potential. Furthermore, differences between absorbed-quantity normalized absorption times is seen between the hydrogen and deuterium absorbates. Sievert's law of absorption is also shown to hold for individual Pd nanoparticles in the α phase.
-
DOI :
10.1021/acsaem.5c00228
 Read more
Read more
Probing Strain in Individual Palladium Nanocrystals during Electrochemically Induced Phase Transitions
C. Atlan*, C. Chatelier, A. Ngoipala, K. Olson, A. Viola, E. Bellec, M. Grimes, B. Gilles, M. Qamar, M. Mrovec, S. Leake, J. Eymery, T. Schülli, M. Vandichel, M.-I. Richard* and F. Maillard*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, XXXX, XXX, XXX-XXX
Citations : 0
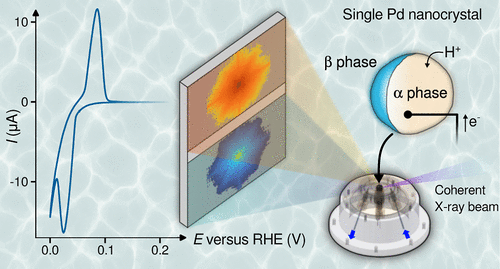
Probing Strain in Individual Palladium Nanocrystals during Electrochemically Induced Phase Transitions
Clément Atlan*, Corentin Chatelier, Apinya Ngoipala, Kyle Olson, Arnaud Viola,Ewen Bellec, Michael Grimes, Bruno Gilles, Minaam Qamar, Matous Mrovec, Steven J. Leake, Joël Eymery, Tobias U. Schülli, Matthias Vandichel, Marie-Ingrid Richard* and Frédéric Maillard*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, XXXX, XXX, XXX-XXX
-
Abstract
The palladium-hydrogen system plays a crucial role in catalysis, hydrogen production and storage, hydrogen embrittlement, and sensing technologies. Understanding the transition of palladium nanocrystals (NCs) from the hydrogen-poor (α) phase to the hydrogen-rich (β) phase is crucial for elucidating hydrogen absorption/desorption mechanisms as well as related phenomena such as hydrogen trapping. In this study, we carefully minimized undesired X-ray beam effects and used in situ Bragg coherent diffraction imaging under electrochemical control to map the strain and lattice parameter distribution within individual palladium NCs across electrochemical potentials relevant to hydrogen absorption and desorption. Lattice parameter changes in both α and β phases are tracked, and reversible strain inversion during the α-to-β phase transition is observed. Through strain and reciprocal space analysis and molecular simulations, a model for the α-to-β phase transition is proposed, which includes a hydrogen-saturated subsurface shell, hydrogen depletion from the α phase during β phase nucleation, and propagation of the β phase in a spherical-cap fashion.
-
DOI :
10.1021/jacs.5c05102
 Read more
Read more
Giant transformation strain and rotation in Ni-Pt nanoparticles caused by atomic ordering
M. Levi, A. Bisht, C. Chatelier, C. Atlan, J. Eymery, S. Leake, P. Boesecke, M.-I. Richard and E. Rabkin*
Acta Materialia, 2025, 294, 121129
Citations : 0
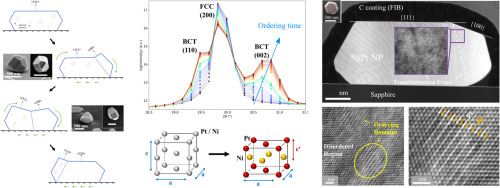
Giant transformation strain and rotation in Ni-Pt nanoparticles caused by atomic ordering
M. Levi, A. Bisht, C. Chatelier, C. Atlan, J. Eymery, S. Leake, P. Boesecke, M.-I. Richard and E. Rabkin*
Acta Materialia, 2025, 294, 121129
-
Abstract
We fabricated single crystalline faceted nanoparticles of near-stoichiometric NiPt alloy employing the solid state dewetting of Ni-Pt bilayers deposited on a sapphire substrate. The particles were annealed within the stability range of the ordered L10 phase. We uncovered recurrent changes of the fraction of disordered (100)-oriented particles, characterized by intermittent disorder-order transformations coupled with particle reorientation. The nucleation and expansion of ordered domains within the disordered (111)-oriented particles resulted in an increase of internal stresses and concomitant nucleation of twinning dislocations. Subsequent out-of-plane rotation via twinning has resulted in intermittent nanoparticles disordering due to the slip geometry in the ordered L10 phase. Notably, the re-orienting particles exhibited a macroscopic linear transformation strain reaching a value of 23 %. The discovery of ordering-induced particle rotation and reorientation in our study introduces a novel approach for engineering the functional properties of supported metal nanoparticles.
-
DOI :
10.1016/j.actamat.2025.121129
 Read more
Read more
Capturing Catalyst Strain Dynamics during Operando CO Oxidation
M. Grimes*, C. Atlan, C. Chatelier, E. Bellec, K. Olson, D. Simonne, M. Levi, T. U. Schülli, S. Leake, E. Rabkin, J. Eymery, and M.-I. Richard*
ACS Nano, 2024, 18(30), 19608-19617
Citations : 0
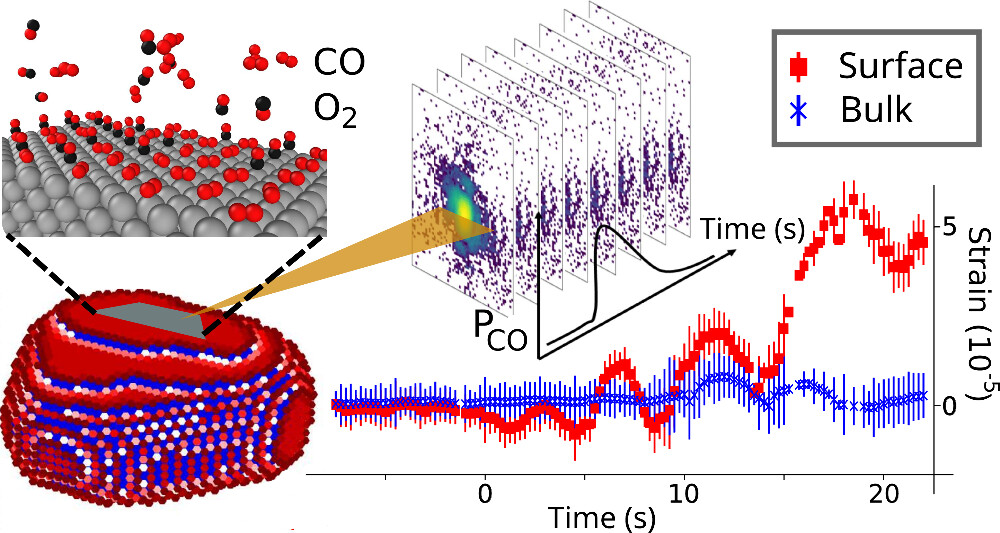
Capturing Catalyst Strain Dynamics during Operando CO Oxidation
Michael Grimes*, Clément Atlan, Corentin Chatelier, Ewen Bellec, Kyle Olson, David Simonne, Mor Levi, Tobias U. Schülli, Seven Leake, Eugen Rabkin, Joël Eymery, and Marie-Ingrid Richard*
ACS Nano, 2024, 18(30), 19608-19617
-
Abstract
Understanding the strain dynamic behavior of catalysts is crucial for the development of cost-effective, efficient, stable, and long-lasting catalysts. Using time-resolved Bragg coherent diffraction imaging at the fourth generation Extremely Brilliant Source of the European Synchrotron (ESRF-EBS), we achieved subsecond time resolution during operando chemical reactions. Upon investigation of Pt nanoparticles during CO oxidation, the three-dimensional strain profile highlights significant changes in the surface and subsurface regions, where localized strain is probed along the [111] direction. Notably, a rapid increase in tensile strain was observed at the top and bottom Pt {111} facets during CO adsorption. Moreover, we detected oscillatory strain changes (6.4 s period) linked to CO adsorption during oxidation, where a time resolution of 0.25 s was achieved. This approach allows for the study of adsorption dynamics of catalytic nanomaterials at the single-particle level under operando conditions, which provides insight into nanoscale catalytic mechanisms.
-
DOI :
10.1021/acsnano.4c04127
 Read more
Read more
Unveiling Core-Shell Structure Formation in a Ni3Fe Nanoparticle with In Situ Multi-Bragg Coherent Diffraction Imaging
C. Chatelier*, C. Atlan, M. Dupraz, S. Leake, N. Li, T. U. Schülli, M. Levi, E. Rabkin, L. Favre, S. Labat, J. Eymery, and M.-I. Richard*
ACS Nano, 2024, 18(21), 13517-13527
Citations : 0
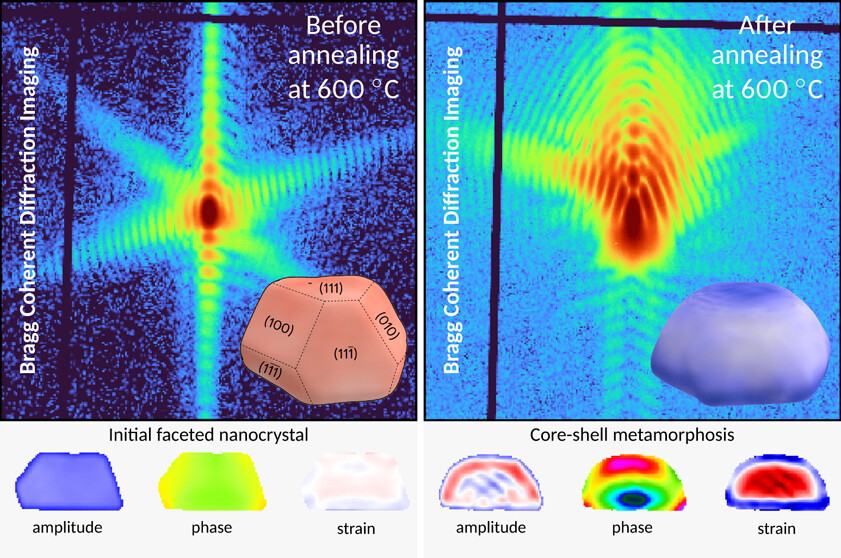
Unveiling Core-Shell Structure Formation in a Ni3Fe Nanoparticle with In Situ Multi-Bragg Coherent Diffraction Imaging
Corentin Chatelier*, Clément Atlan, Maxime Dupraz, Steven Leake, Ni Li, Tobias U. Schülli, Mor Levi, Eugen Rabkin, Luc Favre, Stéphane Labat, Joël Eymery, and Marie-Ingrid Richard*
ACS Nano, 2024, 18(21), 13517-13527
-
Abstract
Solid-state reactions play a key role in materials science. The evolution of the structure of a single 350 nm Ni3Fe nanoparticle, i.e., its morphology (facets) as well as its deformation field, has been followed by applying multireflection Bragg coherent diffraction imaging. Through this approach, we unveiled a demixing process that occurs at high temperatures (600 °C) under an Ar atmosphere. This process leads to the gradual emergence of a highly strained core-shell structure, distinguished by two distinct lattice parameters with a difference of 0.4%. Concurrently, this transformation causes the facets to vanish, ultimately yielding a rounded core-shell nanoparticle. This final structure comprises a Ni3Fe core surrounded by a 40 nm Ni-rich outer shell due to preferential iron oxidation. Providing in situ 3D imaging of the lattice parameters at the nanometer scale while varying the temperature, this study─with the support of atomistic simulations─not only showcases the power of in situ multireflection BCDI but also provides valuable insights into the mechanisms at work during a solid-state reaction characterized by a core-shell transition.
-
DOI :
10.1021/acsnano.3c11534
 Read more
Read more
Taking Bragg Coherent Diffraction Imaging to Higher Energies at Fourth Generation Synchrotrons: Nanoscale Characterization
M.-I. Richard*, I. Martens, M. Dupraz, J. Drnec, V. Honkimäki, C. Chatelier, C. Atlan, M. Mirolo, M. Levi, E. Rabkin, J. Eymery, A. Naidu, T. U. Schülli, and S. J. Leake
ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2023, 12(6), 10246-10255
Citations : 0
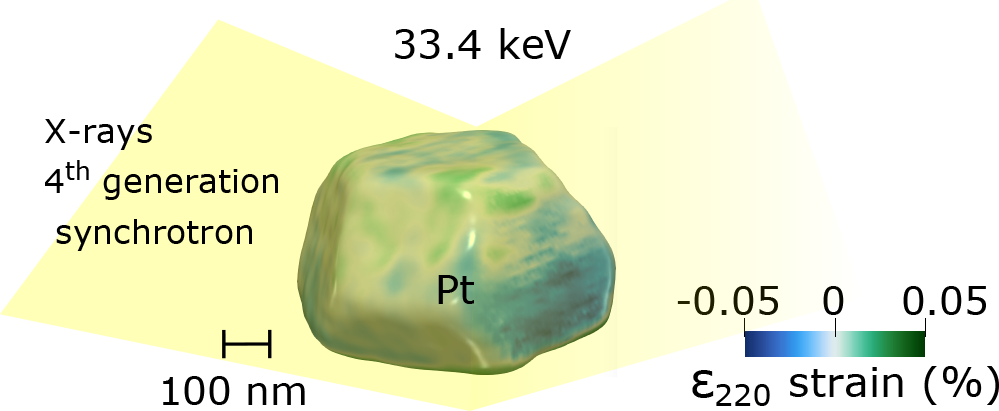
Taking Bragg Coherent Diffraction Imaging to Higher Energies at Fourth Generation Synchrotrons: Nanoscale Characterization
Marie-Ingrid Richard*, Isaac Martens, Maxime Dupraz, Jakub Drnec, Veijo Honkimäki, Corentin Chatelier, Clément Atlan, Marta Mirolo, Mor Levi, Eugen Rabkin, Joël Eymery, Akshata Naidu, Tobias U. Schülli, and Steven J. Leake
ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2023, 12(6), 10246-10255
-
Abstract
High-energy Bragg coherent diffraction imaging (BCDI) can enable three-dimensional imaging of atomic structure within individual crystallites in complex environments. Here, we show that sufficient coherent photon flux is available to extend the BCDI technique to higher energies to (1) obtain improved strain information and sensitivity at the nanoscale with higher order Bragg reflections, (2) exploit BCDI in embedded materials or complex operando environments, (3) reduce X-ray induced sample modification, and (4) minimize dynamical scattering effects. We demonstrate the nanoscale imaging technique on the same sub-micrometer sized crystal at 8.5, 19.9, and 33.4 keV by taking advantage of the brilliance and coherence of the fourth generation EBS of the ID01 beamline at ESRF.
-
DOI :
10.1021/acsanm.3c01145
 Read more
Read more
Imaging the strain evolution of a platinum nanoparticle under electrochemical control
C. Atlan*, C. Chatelier*, I. Martens, M. Dupraz, A. Viola, N. Li, L. Gao, S. Leake, T. Schulli, J. Eymery, F. Maillard*, M.-I. Richard*
Nature Materials, 2023, 22(6), 754-761
Citations : 0
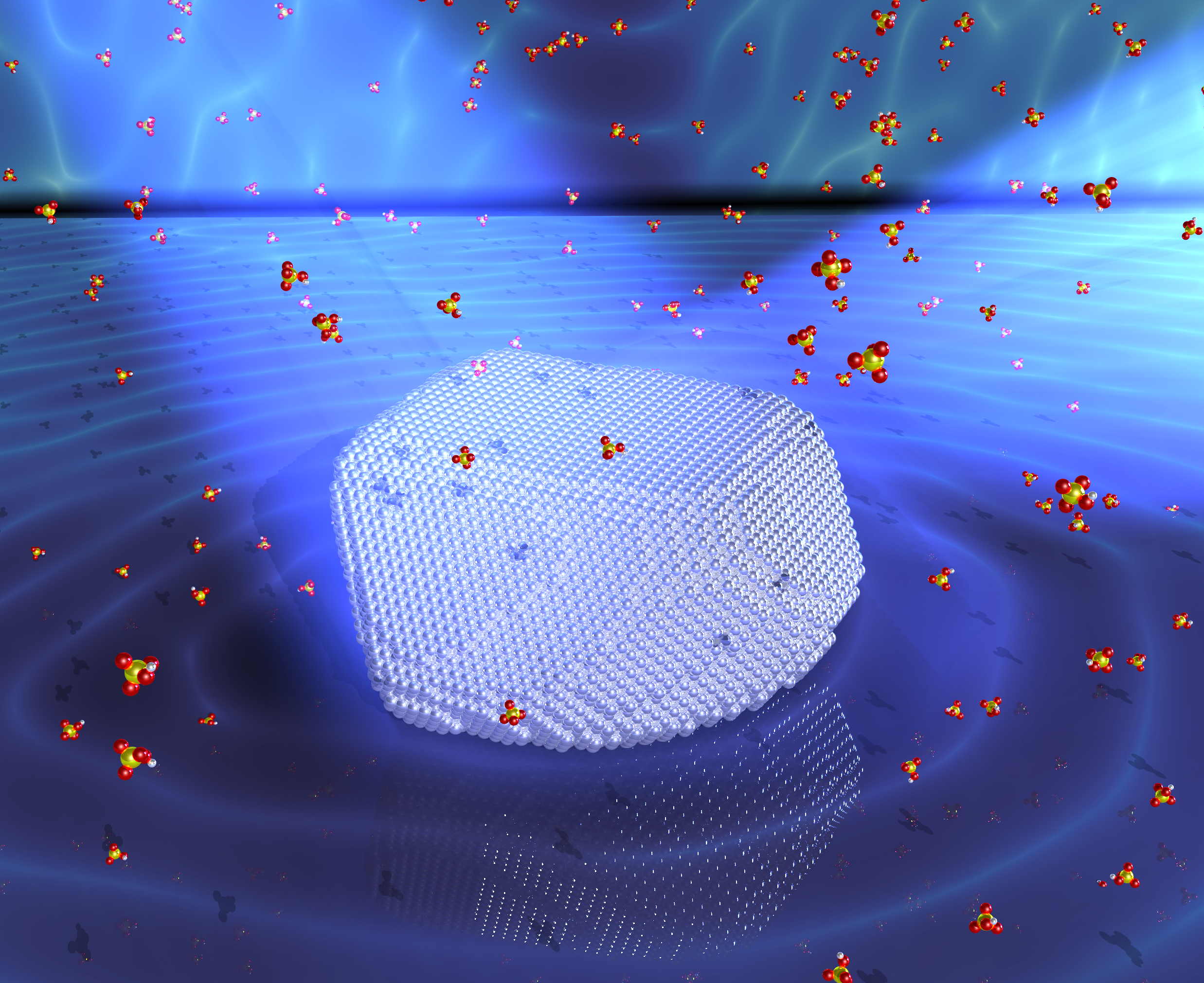
Imaging the strain evolution of a platinum nanoparticle under electrochemical control
Clément Atlan*, Corentin Chatelier*, Isaac Martens, Maxime Dupraz, Arnaud Viola, Ni Li, Lu Gao, Steven Leake, Tobias Schulli, Joël Eymery, Frédéric Maillard*, Marie-Ingrid Richard*
Nature Materials, 2023, 22(6), 754-761
-
Abstract
Surface strain is widely employed in gas phase catalysis and electrocatalysis to control the binding energies of adsorbates on active sites. However, in situ or operando strain measurements are experimentally challenging, especially on nanomaterials. Here we exploit coherent diffraction at the new fourth-generation Extremely Brilliant Source of the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility to map and quantify strain within individual Pt catalyst nanoparticles under electrochemical control. Three-dimensional nanoresolution strain microscopy, together with density functional theory and atomistic simulations, show evidence of heterogeneous and potential-dependent strain distribution between highly coordinated ({100} and {111} facets) and undercoordinated atoms (edges and corners), as well as evidence of strain propagation from the surface to the bulk of the nanoparticle. These dynamic structural relationships directly inform the design of strain-engineered nanocatalysts for energy storage and conversion applications.
-
DOI :
nature.com/articles/s41563-023-01528-x
 Read more
Read more
Revealing the epitaxial interface between Al13Fe4 and Al5Fe2 enabling atomic Al interdiffusion
C. Chatelier, K. Anand, P. Gille, M.-C. de Weerd, J. Ledieu, V. Fournée, A. Resta, A. Vlad, Y. Garreau, A. Coati, É. Gaudry*
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2023, 15(15), 19593-19603
Citations : 0
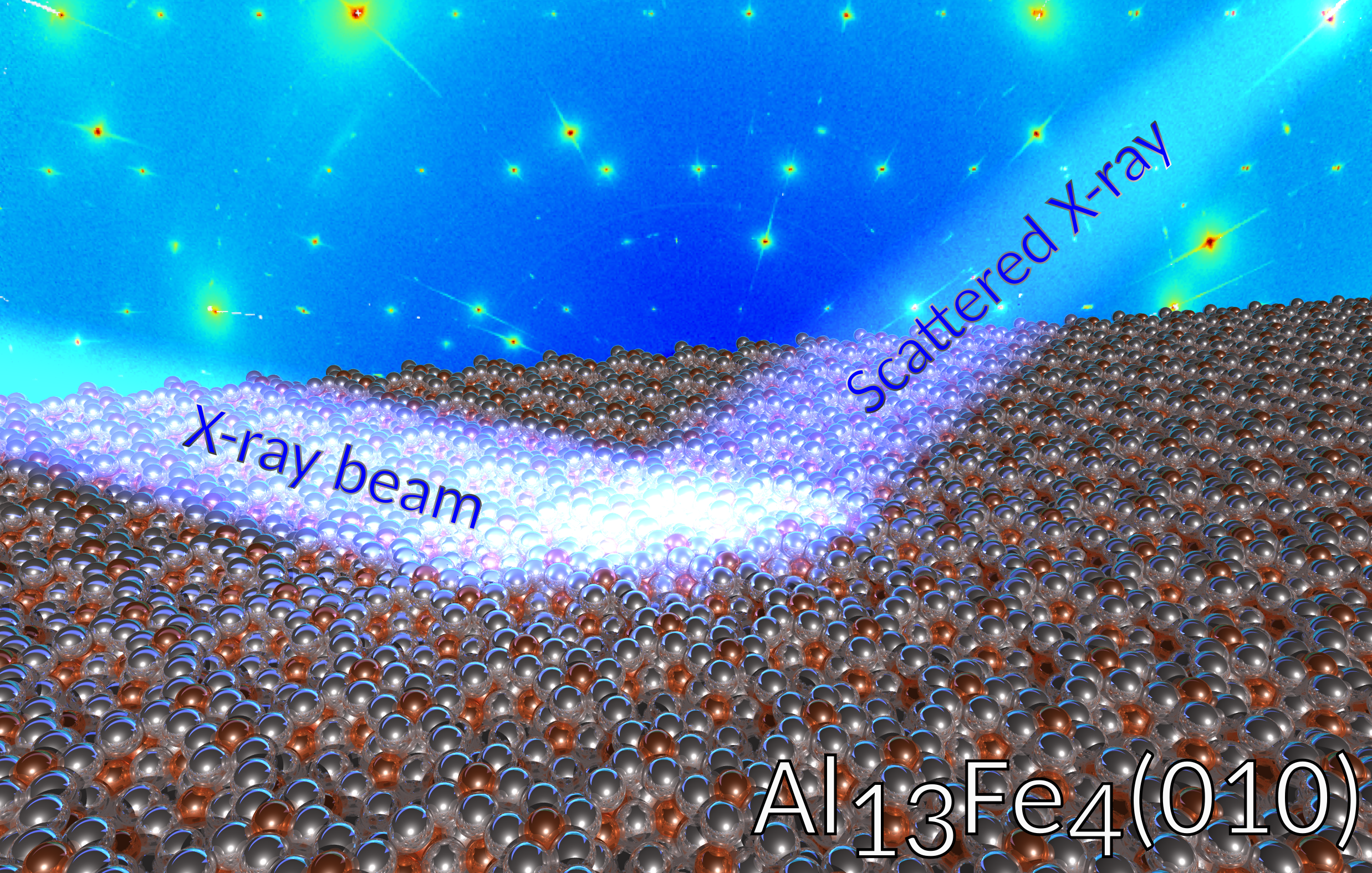
Revealing the epitaxial interface between Al13Fe4 and Al5Fe2 enabling atomic Al interdiffusion
Corentin Chatelier, Kanika Anand, Peter Gille, Marie-Cécile de Weerd, Julian Ledieu, Vincent Fournée, Andrea Resta, Alina Vlad, Yves Garreau, Alessandro Coati, Émilie Gaudry*
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2023, 15(15), 19593-19603
-
Abstract
Steel is the most commonly manufactured material in the world. Its performances can be improved by hot-dip coating with the low weight aluminum metal. The structure of the Al∥Fe interface, which is known to contain a buffer layer made of complex intermetallic compounds such as Al5Fe2 and Al13Fe4, is crucial for the properties. On the basis of surface X-ray diffraction, combined with theoretical calculations, we derive in this work a consistent model at the atomic scale for the complex Al13Fe4(010)∥Al5Fe2(001) interface. The epitaxial relationships are found to be [130]Al5Fe2∥[010]Al13Fe4 and [110]Al5Fe2∥[100]Al13Fe4. Molecular dynamics simulations suggest a mechanism of Al diffusion to explain the formation of the complex Al13Fe4 and Al5Fe2 phases at the Al∥Fe interface.
-
DOI :
10.1021/acsami.2c22886
 Read more
Read more
Gwaihir: Jupyter Notebook graphical user interface for Bragg Coherent Diffraction Imaging
D. Simonne*, J. Carnis, C. Atlan, C. Chatelier, V. Favre-Nicolin, M. Dupraz, S. J. Leake, A. Resta, A. Coati, M.-I. Richard
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2022, 55(4), 1045-1054
Citations : 0
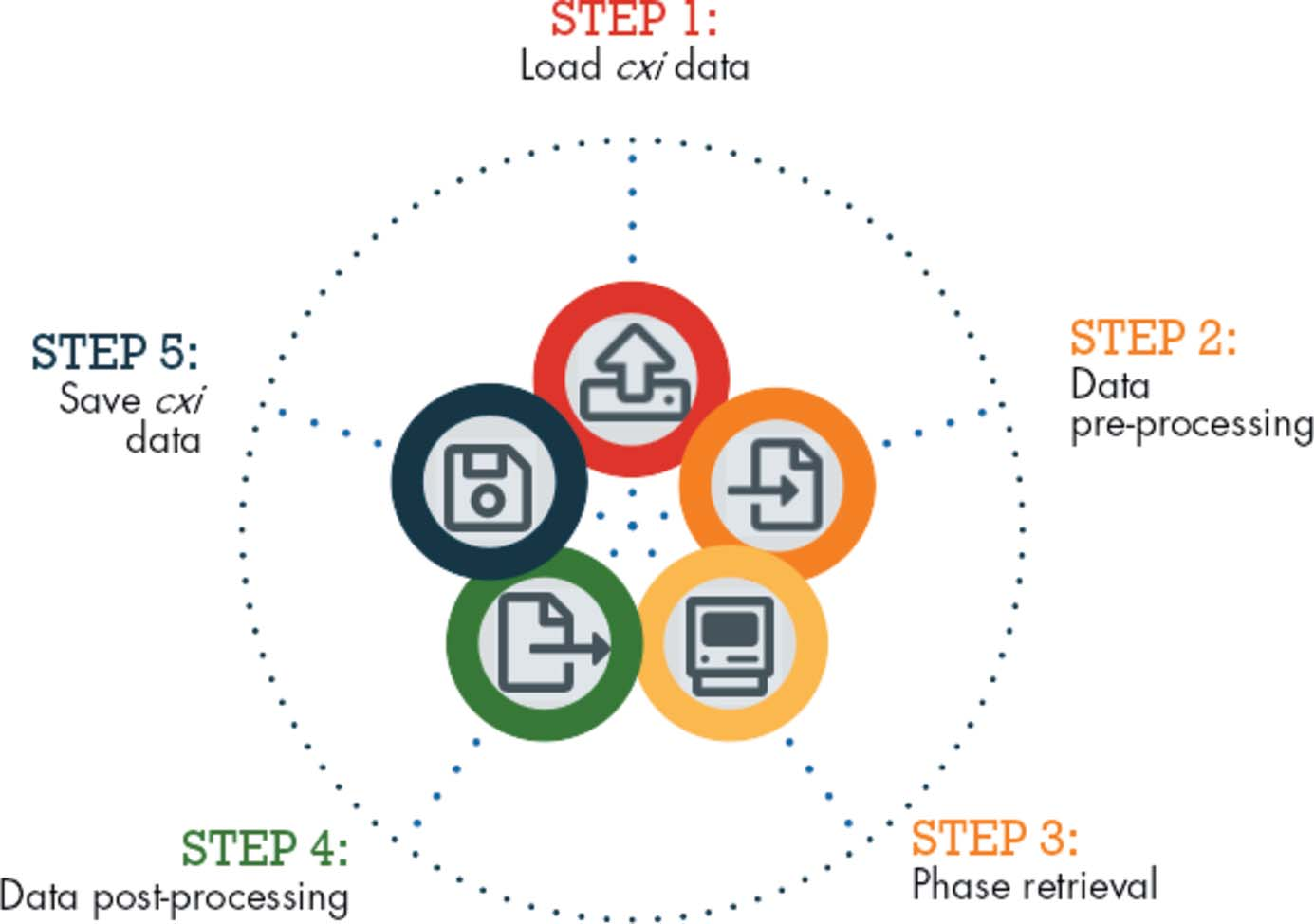
Gwaihir: Jupyter Notebook graphical user interface for Bragg Coherent Diffraction Imaging
David Simonne*, Jérôme Carnis, Clément Atlan, Corentin Chatelier, Vincent Favre-Nicolin, Maxime Dupraz, Steven J. Leake, Andrea Resta, Alessandro Coati, Marie-Ingrid Richard
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2022, 55(4), 1045-1054
-
Abstract
Bragg coherent X-ray diffraction is a nondestructive method for probing material structure in three dimensions at the nanoscale, with unprecedented resolution in displacement and strain fields. This work presents Gwaihir, a user-friendly and open-source tool to process and analyze Bragg coherent X-ray diffraction data. It integrates the functionalities of the existing packages bcdi and PyNX in the same toolbox, creating a natural workflow and promoting data reproducibility. Its graphical interface, based on Jupyter Notebook widgets, combines an interactive approach for data analysis with a powerful environment designed to link large-scale facilities and scientists.
-
DOI :
10.1107/S1600576722005854
 Read more
Read more
Imaging the facet surface strain state of supported multi-faceted Pt nanoparticles during reaction
M. Dupraz*, N. Li, J. Carnis, L. Wu, S. Labat, C. Chatelier, R. van de Poll, J. P. Hofmann, E. Almog, S. J. Leake, Y. Watier, S. Lazarev, F. Westermeier, M. Sprung, E. J. M. Hensen, O. Thomas, E. Rabkin, Marie-Ingrid Richard*
Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1), 3529
Citations : 0
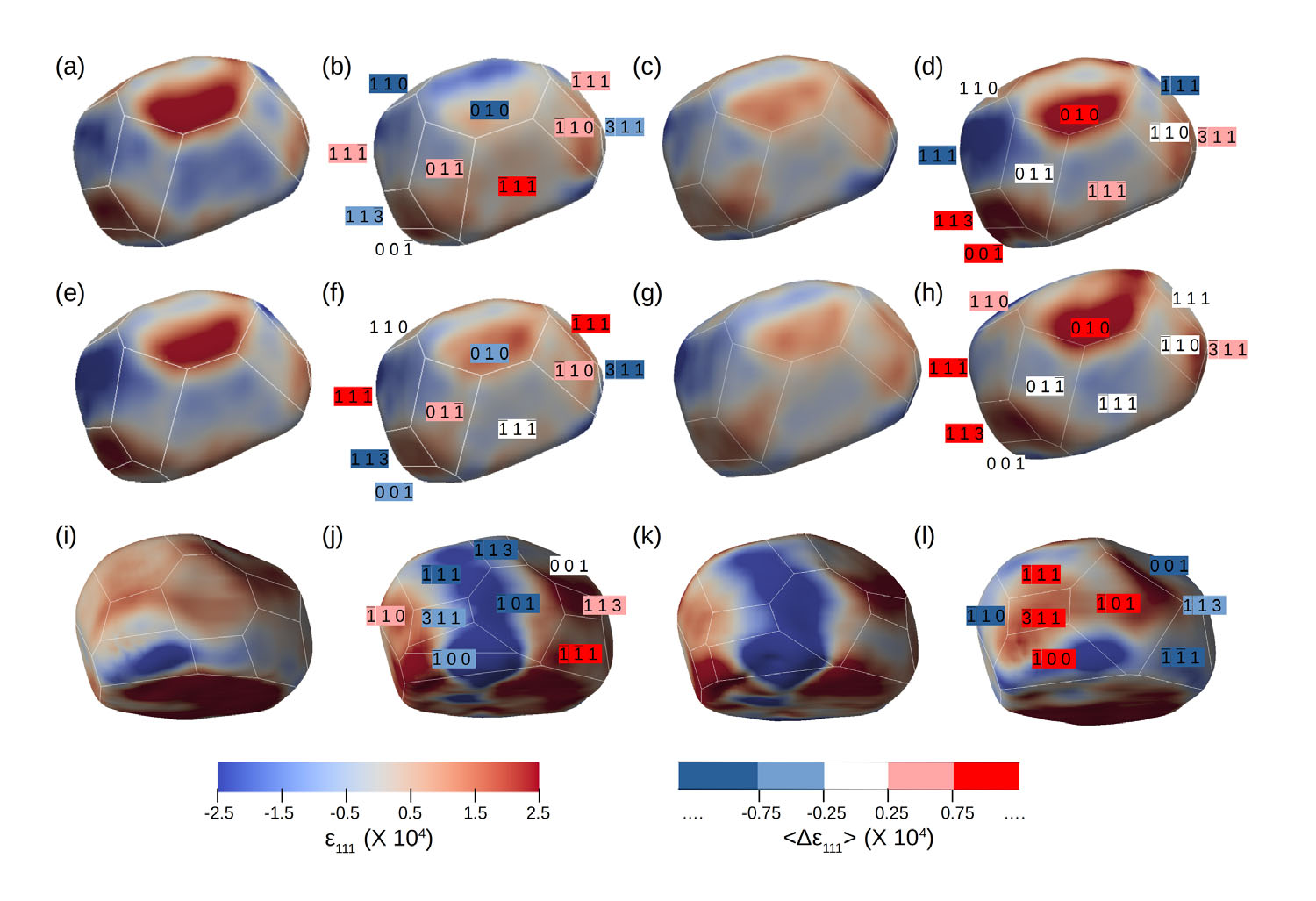
Imaging the facet surface strain state of supported multi-faceted Pt nanoparticles during reaction
Maxime Dupraz*, Ni Li, Jérôme Carnis, Longfei Wu, Stéphane Labat, Corentin Chatelier, Rim van de Poll, Jan P. Hofmann, Ehud Almog, Steven J. Leake, Yves Watier, Sergey Lazarev, Fabian Westermeier, Michael Sprung, Emiel J. M. Hensen, Olivier Thomas, Eugen Rabkin, Marie-Ingrid Richard*
Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1), 3529
-
Abstract
Nanostructures with specific crystallographic planes display distinctive physico-chemical properties because of their unique atomic arrangements, resulting in widespread applications in catalysis, energy conversion or sensing. Understanding strain dynamics and their relationship with crystallographic facets have been largely unexplored. Here, we reveal in situ, in three-dimensions and at the nanoscale, the volume, surface and interface strain evolution of single supported platinum nanocrystals during reaction using coherent x-ray diffractive imaging. Interestingly, identical {hkl} facets show equivalent catalytic response during non-stoichiometric cycles. Large strain variations are observed in localised areas, in particular in the vicinity of the substrate/particle interface, suggesting a significant influence of the substrate on the reactivity. These findings will improve the understanding of dynamic properties in catalysis and related fields.
-
DOI :
nature.com/articles/s41467-022-30592-1
 Read more
Read more
Two-dimensional oxide quasicrystal approximants with tunable electronic and magnetic properties
T. Trevizam Dorini, F. Brix, C. Chatelier, A. Kokalj, É. Gaudry*
Nanoscale, 2021, 13, 10771-10779
Citations : 0
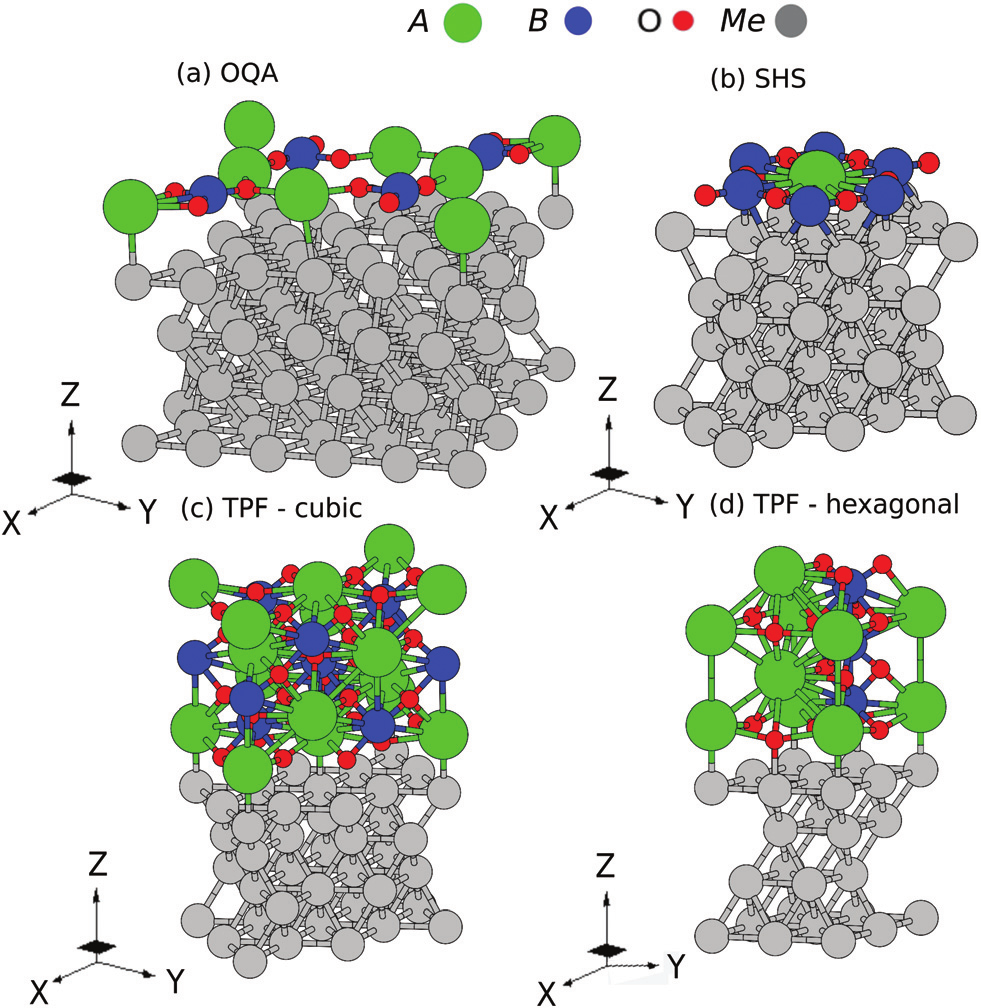
Two-dimensional oxide quasicrystal approximants with tunable electronic and magnetic properties
Thiago Trevizam Dorini, Florian Brix, Corentin Chatelier, Anton Kokalj, Émilie Gaudry*
Nanoscale, 2021, 13, 10771-10779
-
Abstract
Recently, the discovery of the quasiperiodic order in ultra-thin perovskite films reinvigorated the field of 2-dimensional oxides on metals, and raised the question of the reasons behind the emergence of the quasiperiodic order in these systems. The effect of size-mismatch between the two separate systems has been widely reported as a key factor governing the formation of new oxide structures on metals. Herein, we show that electronic effects can play an important role as well. To this end, the structural, thermodynamic, electronic and magnetic properties of freestanding two-dimensional oxide quasicrystalline approximants and their characteristics when deposited over metallic substrates are systematically investigated to unveil the structure-property relationships within the series. Our thermodynamic approach suggests that the formation of these aperiodic systems is likely for a wide range of compositions. This work provides well-founded general insights into the driving forces behind the emergence of the quasiperiodic order in ternary oxides grown on elemental metals and offers guidelines for the discovery of new oxide quasicrystalline ultra-thin films with interesting physical properties.
-
DOI :
10.1039/D1NR02407H
 Read more
Read more
On the surface structures and catalytic properties of Al-based intermetallics
Corentin Chatelier
PhD thesis, Université de Lorraine, 2021
Citations : 0
On the surface structures and catalytic properties of Al-based intermetallics
Corentin Chatelier
PhD thesis, Université de Lorraine, 2021
-
Abstract
Replacing noble metal (Pd, Pt, Au) catalysts with inexpensive, environmentally harmless, active, selective, and stable substitutes is a big challenge for the chemical industry. Several aluminium-based complex intermetallic compounds have shown promises for alkynes and alkenes hydrogenation reactions, which are of interest in the chemical industry. It is the case for Al5Co2, Al13Co4 and Al13Fe4 quasicrystalline approximants. The study of their catalytic properties demands different approaches, both theoretical and experimental, in order to determine first their surface structures under ultra-high vacuum or reaction conditions, then their catalytic properties. The combination of surface science experiments (scanning tunneling microscopy, surface X-ray diffraction) and theoretical chemistry calculations (surface energies, adsorption energies and reaction pathways) allows for a better understanding of the key parameters behind the promising catalytic properties of these materials.
-
DOI :
hal.univ-lorraine.fr/tel-03254779
 Read more
Read more
Ammonia oxidation over a Pt25Rh75(001) model catalyst surface: an operando study
A. Resta*, U. Hejral, S. Blomberg, S. Albertin, A. Vlad, Y. Garreau, C. Chatelier, F. Venturini, P. Ferrer-Escorihuela, G. Held, D. Grinter, E. Lundgren, A. Coati
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(40), 22192-22199
Citations : 0
Ammonia oxidation over a Pt25Rh75(001) model catalyst surface: an operando study
Andrea Resta*, Uta Hejral, Sara Blomberg, Stefano Albertin, Alina Vlad, Yves Garreau, Corentin Chatelier, Federica Venturini, Pilar Ferrer-Escorihuela, Georg Held, Dave Grinter, Edvin Lundgren, Alessandro Coati
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(40), 22192-22199
 Read more
Read more
Pseudo-2-fold surface of the Al13Co4 catalyst: structure, stability, and hydrogen adsorption
C. Chatelier, Y. Garreau, A. Vlad, J. Ledieu, A. Resta, V. Fournée, M.-C. de Weerd, A. Coati, É. Gaudry*
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2020, 12(35), 39787-39797
Citations : 0
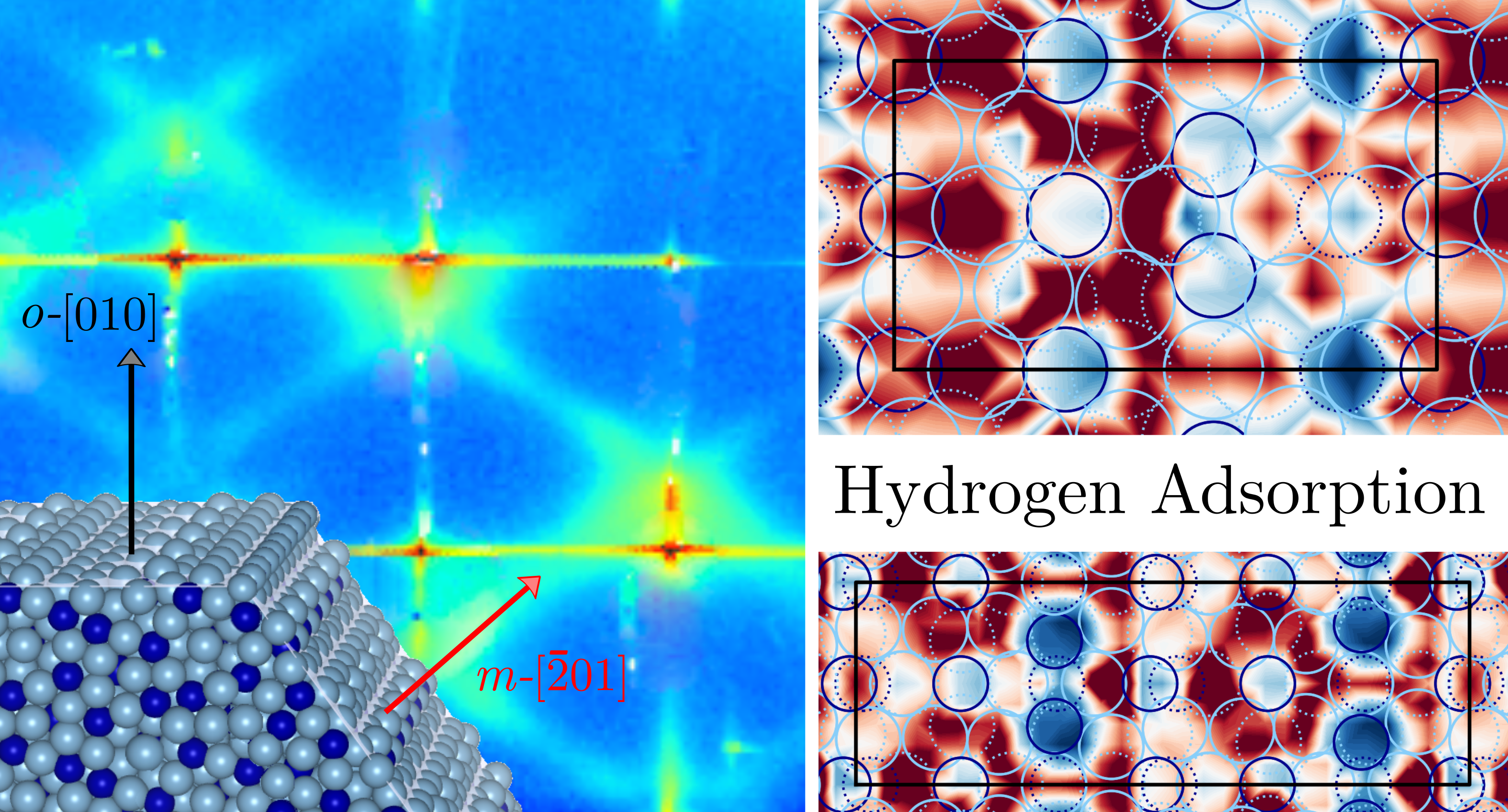
Pseudo-2-fold surface of the Al13Co4 catalyst: structure, stability, and hydrogen adsorption
Corentin Chatelier, Yves Garreau, Alina Vlad, Julian Ledieu, Andrea Resta, Vincent Fournée, Marie-Cécile de Weerd, Alessandro Coati, Émilie Gaudry*
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2020, 12(35), 39787-39797
-
Abstract
A few low-order approximants to decagonal quasicrystals have been shown to provide excellent activity and selectivity for the hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes. It is the case for the Al13Co4 compound, for which the catalytic properties of the pseudo-2-fold orientation have been revealed to be among the best. A combination of surface science studies, including surface X-ray diffraction, and calculations based on density functional theory is used here to derive an atomistic model for the pseudo-2-fold o-Al13Co4 surface, whose faceted and columnar structure is found very similar to the one of the 2-fold surface of the d-Al-Ni-Co quasicrystal. Facets substantially stabilize the system, with energies in the range 1.19-1.31 J/m2, i.e., much smaller than the ones of the pseudo-10-fold (1.49-1.68 J/m2) and pseudo-2-fold (1.66 J/m2) surfaces. Faceting is also a main factor at the origin of the Al13Co4 catalytic performances, as illustrated by the comparison of the pseudo-10-fold, pseudo-2-fold and facet potential energy maps for hydrogen adsorption. This work gives insights toward the design of complex intermetallic catalysts through surface nanostructuration for optimized catalytic performances.
-
DOI :
10.1021/acsami.0c09702
 Read more
Read more
Catalytic activation of a non-noble intermetallic surface through nanostructuration under hydrogenation conditions revealed by atomistic thermodynamics
É. Gaudry*, C. Chatelier, D. Loffreda, D. Kandaskalov, A. Coati, L. Piccolo
Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8, 7422-7431
Citations : 0
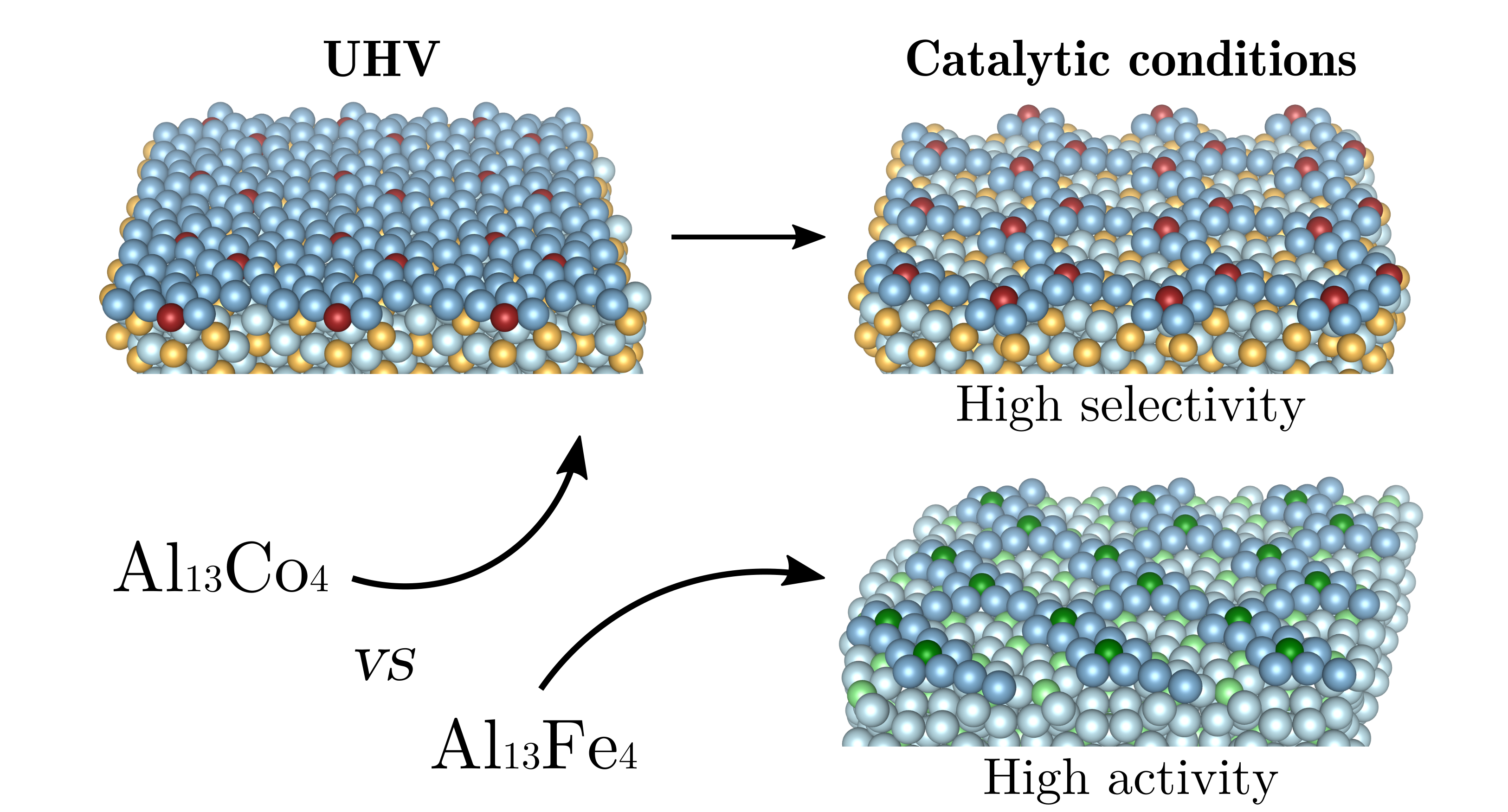
Catalytic activation of a non-noble intermetallic surface through nanostructuration under hydrogenation conditions revealed by atomistic thermodynamics
Émilie Gaudry*, Corentin Chatelier, David Loffreda, Dmytro Kandaskalov, Alessandro Coati, Laurent Piccolo
Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8, 7422-7431
-
Abstract
The unique electronic and crystallographic structure of intermetallics is known to result in excellent catalytic performances for selected chemical reactions. Moreover, owing to the specific bonding network of these compounds, a high structural stability of their surfaces is generally assumed, even under reaction conditions. Transition metal (TM = Fe and Co) aluminides of the Al13TM4 stoichiometry have been previously demonstrated to exhibit high activities and selectivities in partial hydrogenation of alkynes and alkadienes. Focusing on the Al13Co4(100) surface as a model catalyst for butadiene hydrogenation, the hydrogen-rich reaction conditions are predicted - based on DFT calculations and atomistic thermodynamics - to modify the relatively flat surface structure identified under ultra-high vacuum, in the form of highly cohesive clusters emerging from the bulk lattice.
This work demonstrates that a realistic description of surface structures under reaction conditions is mandatory for designing new-generation catalysts based on the complex topology of intermetallic surfaces.
-
DOI :
10.1039/D0TA01146K
 Read more
Read more
From the Surface Structure to Catalytic Properties of Al5Co2(210): A Study Combining Experimental and Theoretical Approaches
C. Chatelier, Y. Garreau, L. Piccolo, A. Vlad, A. Resta, J. Ledieu, V. Fournée, M.-C. de Weerd, F.-E. Picca, M. de Boissieu, R. Felici, A. Coati, É. Gaudry*
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(8), 4552-4562
Citations : 0
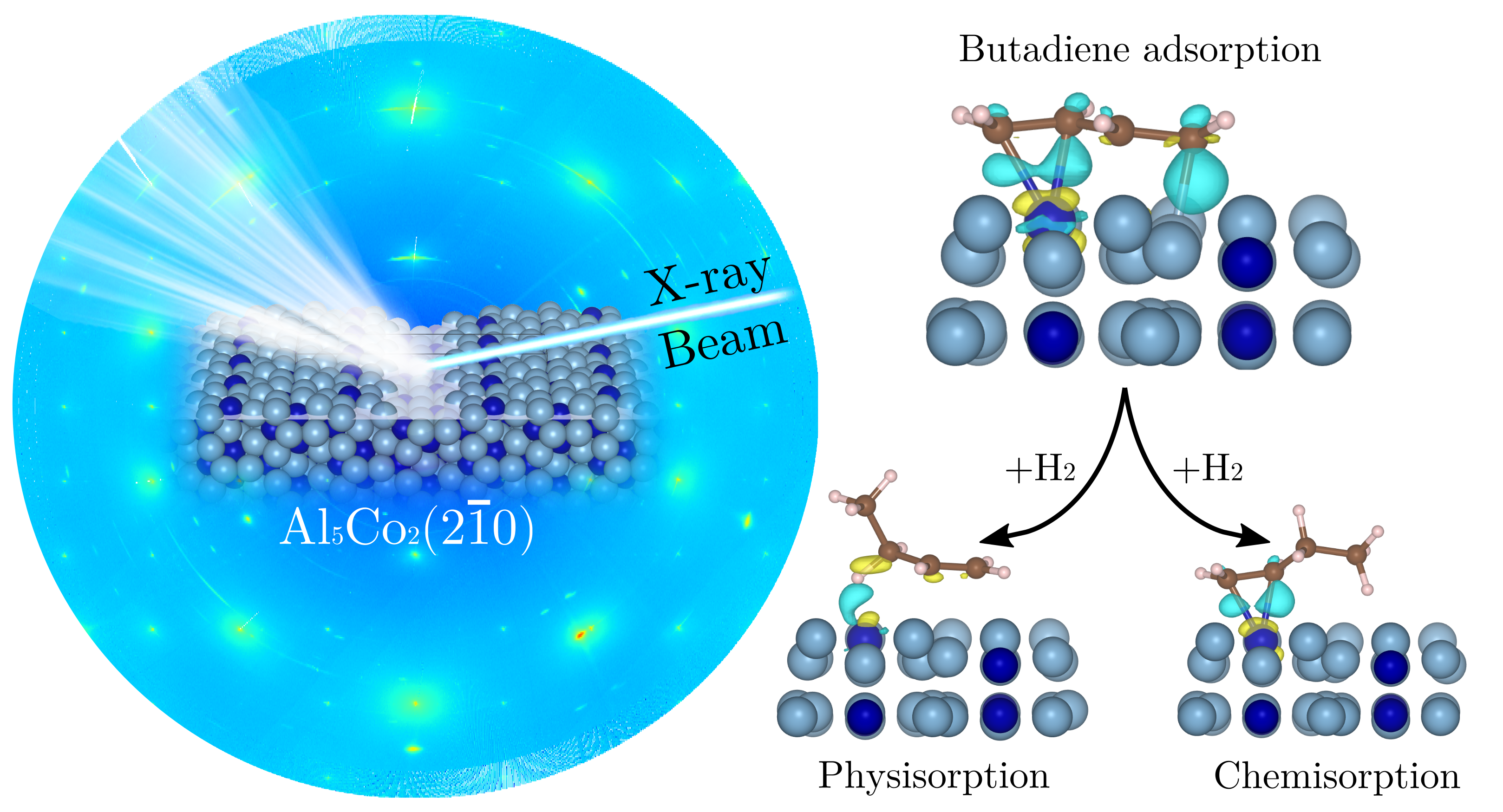
From the Surface Structure to Catalytic Properties of Al5Co2(210): A Study Combining Experimental and Theoretical Approaches
Corentin Chatelier, Yves Garreau, Laurent Piccolo, Alina Vlad, Andrea Resta, Julian Ledieu, Vincent Fournée, Marie-Cécile de Weerd, Frédéric-Emmanuel Picca, Marc de Boissieu, Roberto Felici, Alessandro Coati, Émilie Gaudry*
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(8), 4552-4562
-
Abstract
Replacing noble metal catalysts with inexpensive, environmentally harmless, active, selective, and stable substitutes is a great challenge for the chemical industry. In this paper, the noble metal-free Al5Co2(210) complex intermetallic surface is experimentally identified as active and selective for the semihydrogenation of butadiene. The catalyst surface structure and chemical composition are determined by experimental techniques—surface X-ray diffraction (SXRD) and scanning tunneling microscopy—combined with ab initio calculations. Theoretical investigations of the adsorption properties under reaction conditions demonstrate that the surface Co atomic density drastically impacts the thermodynamic feasibility of the hydrogenation reaction, and they provide information on the reaction mechanism. This work offers insights into the rational design of Al-based catalysts for hydrocarbon hydrogenation reactions.
-
DOI :
10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b09675
 Read more
Read more
Catalytic properties of Al13TM4 complex intermetallics: influence of the transition metal and the surface orientation on butadiene hydrogenation
L. Piccolo*, C. Chatelier, M.-C. de Weerd, F. Morfin, J. Ledieu, V. Fournée, P. Gille, É. Gaudry*
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2019, 20(1), 557-567
Citations : 0
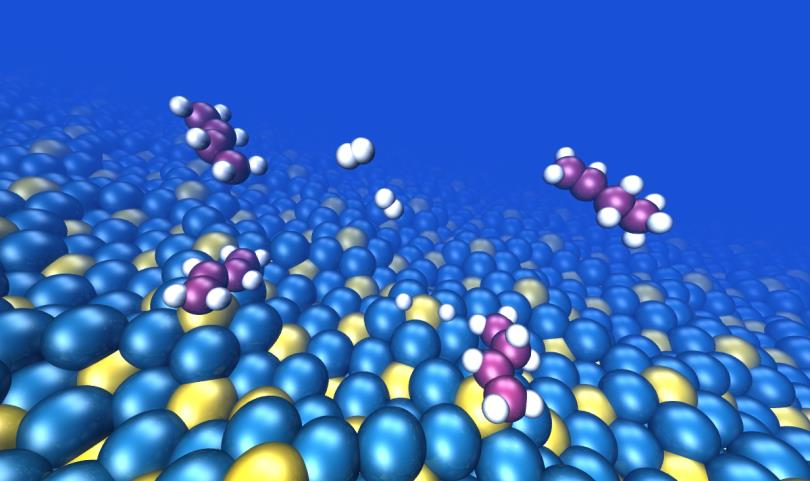
Catalytic properties of Al13TM4 complex intermetallics: influence of the transition metal and the surface orientation on butadiene hydrogenation
Laurent Piccolo*, Corentin Chatelier, Marie-Cécile de Weerd, Franck Morfin, Julian Ledieu, Vincent Fournée, Peter Gille, Émilie Gaudry*
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2019, 20(1), 557-567
-
Abstract
Complex intermetallic compounds such as transition metal (TM) aluminides are promising alternatives to expensive Pd-based catalysts, in particular for the semi-hydrogenation of alkynes or alkadienes. Here, we compare the gas-phase butadiene hydrogenation performances of o-Al13Co4(100), m-Al13Fe4(010) and m-Al13Ru4(010) surfaces, whose bulk terminated structural models exhibit similar cluster-like arrangements. Moreover, the effect of the surface orientation is assessed through a comparison between o-Al13Co4(100) and o-Al13Co4(010).
DFT calculations show that the activity and selectivity results can be rationalized through the determination of butadiene and butene adsorption energies; in contrast, hydrogen adsorption energies do not scale with the catalytic activities. Moreover, the calculation of projected densities of states provides an insight into the Al13TM4 surface electronic structure. Isolating the TM active centers within the Al matrix induces a narrowing of the TM d-band, which leads to the high catalytic performances of Al13TM4 compounds.
-
DOI :
10.1080/14686996.2019.1608792
 Read more
Read more
Bonding network and stability of clusters: the case study of the Al13TM4 pseudo-10fold surfaces
P. Scheid, C. Chatelier, J. Ledieu, V. Fournée, É. Gaudry*
Acta Crystallographica Section A: Foundations and Advances, 2019, 75(2), 314-324
Citations : 0
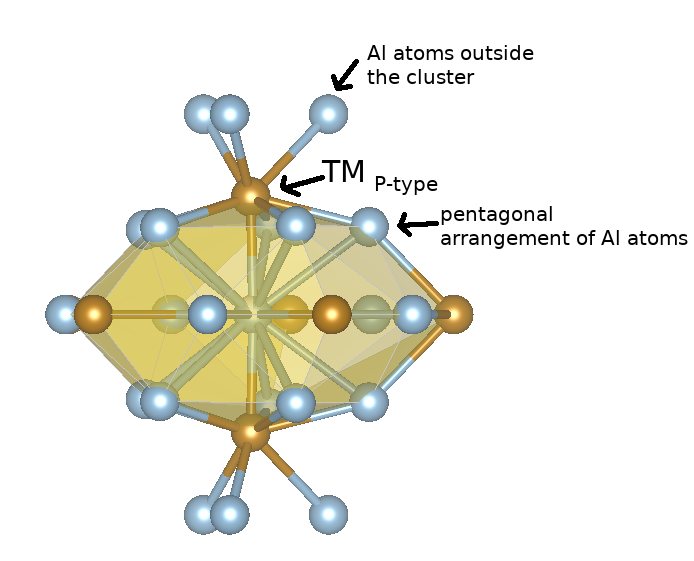
Bonding network and stability of clusters: the case study of the Al13TM4 pseudo-10fold surfaces
Philippe Scheid*, Corentin Chatelier, Julian Ledieu, Vincent Fournée, Émilie Gaudry
Acta Crystallographica Section A: Foundations and Advances, 2019, 75(2), 314-324
-
Abstract
Clusters, i.e. polyhedral geometric entities, are widely used to describe the structure of complex intermetallic compounds. However, little is generally known about their physical significance. The atomic and electronic structures of the Al13TM4 complex intermetallic compounds (TM = Fe, Co, Ru, Rh) have been investigated using a wide range of ab initio tools in order to examine the influence of the chemical composition on the pertinence of the bulk structure description based on 3D clusters. In addition, since surface studies were found to be a relevant approach to address the question of cluster stability in complex phases, the interplay of the cluster substructure with the 2D surface is addressed in the case of the Al13Co4(100) and Al13Fe4(010) surfaces.
-
DOI :
10.1107/S2053273319000202
 Read more
Read more
The Effect of Skelp Thickness on Precipitate Size and Morphology for X70 Microalloyed Steel Using Rietveld Refinement (Quantitative X-ray Diffraction)
C. Chatelier, J. B. Wiskel*, D. G. Ivey, H. Henein*
Crystals, 2018, 8(7), 287
Citations : 0
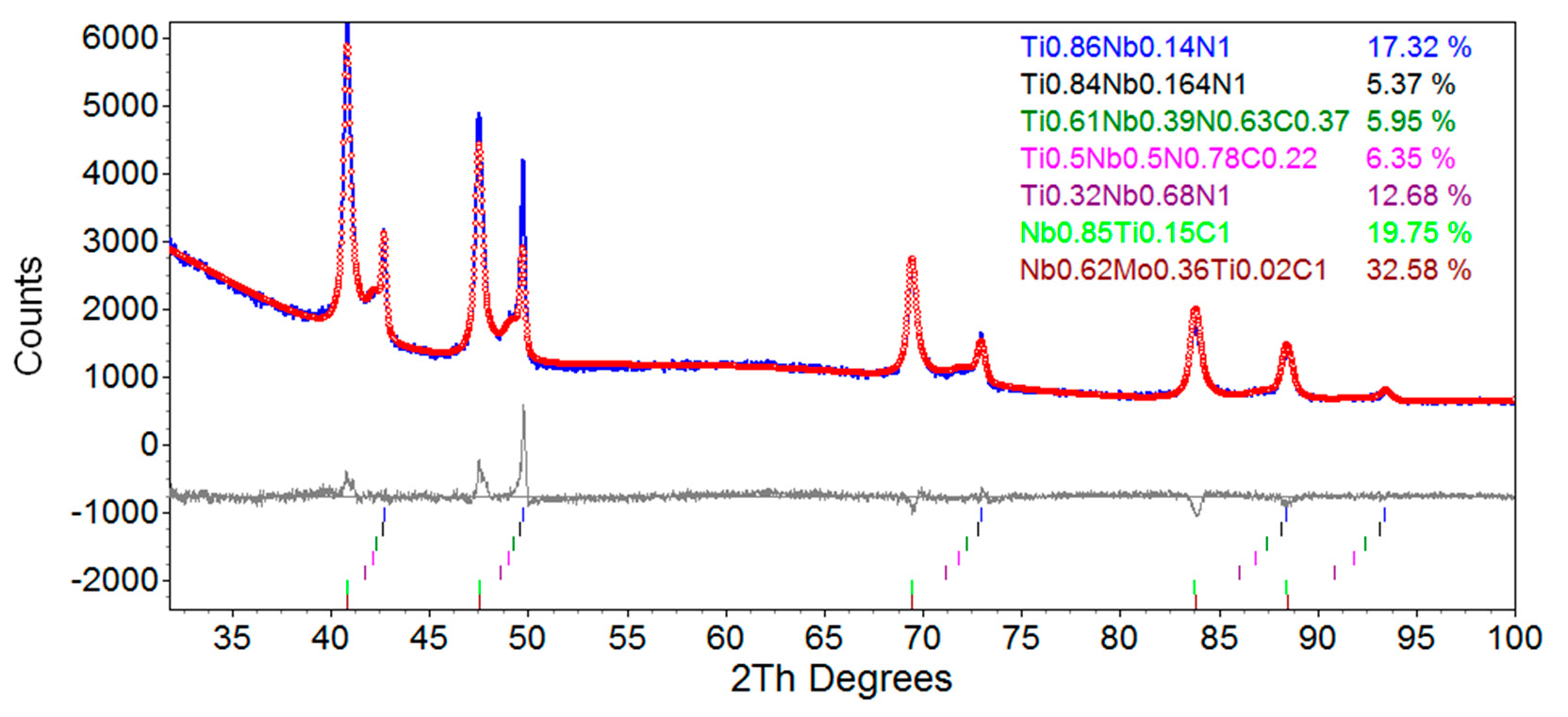
The Effect of Skelp Thickness on Precipitate Size and Morphology for X70 Microalloyed Steel Using Rietveld Refinement (Quantitative X-ray Diffraction)
Corentin Chatelier, J. Barry Wiskel*, Douglas G. Ivey, Hani Henein*
Crystals, 2018, 8(7), 287
-
Abstract
Precipitates in thin-walled (11 mm) and thick-walled X70 (17 mm) microalloyed X70 pipe steel are characterized using Rietveld refinement (a.k.a. quantitative X-ray diffraction (QXRD)), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analyses. Rietveld refinement is done to quantify the relative abundance, compositions, and size distribution of the precipitates. EDX and ICP analyses are undertaken to confirm Rietveld refinement analysis. The volume fraction of large precipitates (1 to 4 μm—mainly TiN rich precipitates) is determined to be twice as high in the thick-walled X70 steel (0.07%). Nano-sized precipitates (< 20 nm) in the thin-walled steel exhibit a higher volume fraction (0.113%) than in the thick-walled steel (0.064%). The compositions of the nano-sized precipitates are similar for both steels.
-
DOI :
10.3390/cryst8070287
 Read more
Read more
Precipitation Analysis in Microalloyed X70 Steels and Heat Treated L80 and T95 Steels
Corentin Chatelier
Master's thesis, University of Alberta, 2017
Citations : 0
Precipitation Analysis in Microalloyed X70 Steels and Heat Treated L80 and T95 Steels
Corentin Chatelier
Master's thesis, University of Alberta, 2017
 Read more
Read more
Structure of the Al13Co4(100) surface: Combination of surface x-ray diffraction and ab initio calculations
É. Gaudry*, C. Chatelier, G. M. McGuirk, L. N. Serkovic-Loli, M.-C. de Weerd, J. Ledieu, V. Fournée, R. Felici, J. Drnec, G. Beutier, M. de Boissieu
Physical Review B, 2016, 94(16), 165406
Citations : 0
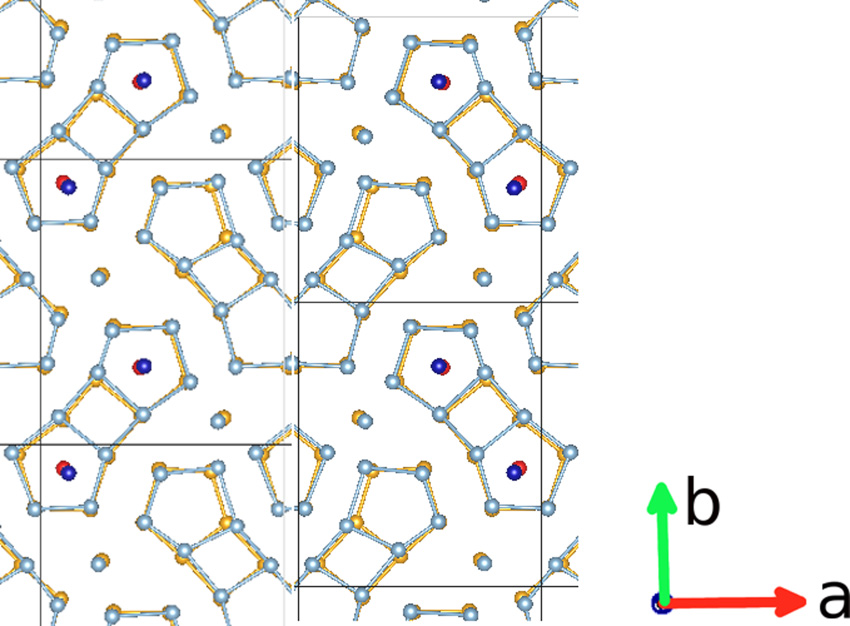
Structure of the Al13Co4(100) surface: Combination of surface x-ray diffraction and ab initio calculations
Émilie Gaudry*, Corentin Chatelier, Gary M. McGuirk, Laura N. Serkovic-Loli, Marie-Cécile de Weerd, Julian Ledieu, Vincent Fournée, Roberto Felici, Jakub Drnec, Guillaume Beutier, Marc de Boissieu
Physical Review B, 2016, 94(16), 165406
-
Abstract
The structure of the quasicrystalline approximant Al13Co4 (100) has been determined by surface x-ray diffraction (SXRD) and complementary density-functional-theory (DFT) calculations. Thanks to the use of a two-dimensional pixel detector, which speeds up the data acquisition enormously, an exceptionally large set of experimental data, consisting of 124 crystal truncation rods, has been collected and used to refine this complex structure of large unit cell and low symmetry. Various models were considered for the SXRD analysis. The best fit is consistent with a surface termination at the puckered type of planes but with a depletion of the protruding Co atoms. The surface energy of the determined surface model was calculated using DFT, and it takes a rather low value of 1.09 J/m2. The results for the atomic relaxation of surface planes found by SXRD or DFT were in excellent agreement. This work opens up additional perspectives for the comprehension of related quasicrystalline surfaces.
-
DOI :
10.1103/PhysRevB.94.165406